Rendering
What is Ray Tracing and How Does it Differ From Other Rendering Techniques?
Ray tracing is a revolutionary rendering technique that has changed the game in the world of computer graphics. It allows for incredibly lifelike images to be produced by simulating how light interacts with objects in a scene. In contrast to other rendering methods, such as rasterization or ray casting, ray tracing provides much more detailed and accurate visual representations of 3D objects and environments. In this blog post, we'll explore what ray tracing is and how it works, highlighting the key differences between it and other rendering techniques. Whether you're a seasoned developer or simply curious about the world of computer graphics, this article will provide you with a deeper understanding of this cutting-edge technology.
- 1. Introduction to Ray Tracing as a Rendering Technique
- 2. Understanding Path Tracing and Ray Tracing
- 3. The Importance of Ray Tracing in Modern Movies
- 4. Addressing Noise Artifacts in Ray Tracing
- 5. Denoising Techniques in Ray Tracing
- 6. Difference Between Ray Tracing and Light Transport Algorithms
- 7. Realism and Benefits of Ray Tracing in 3D Rendering
- 8. Features of Ray Tracing: Shadows, Reflections, and Refractions
- 9. Ray Tracing for Faster Rendering with Motion Blur
- 10. Limitations and Drawbacks of Ray Tracing Techniques
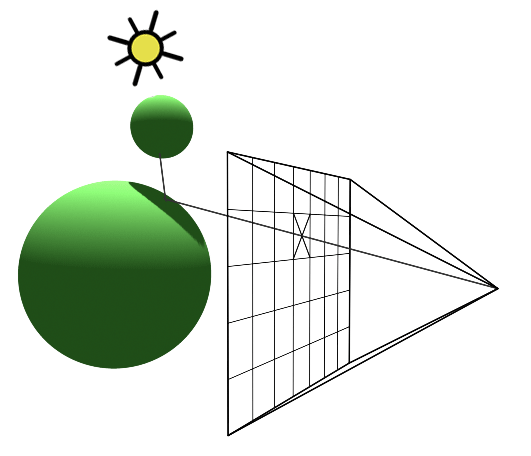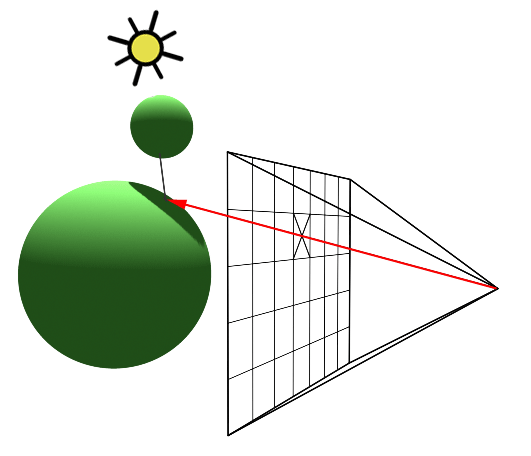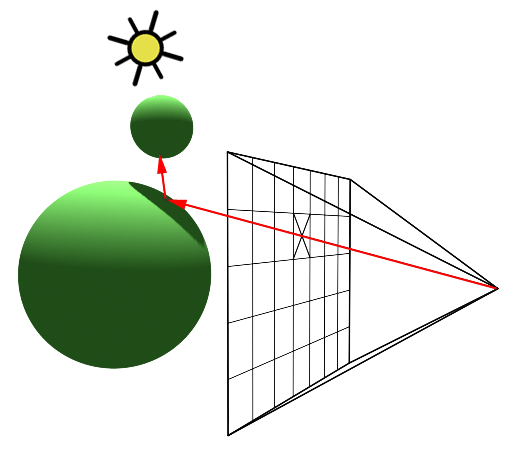
1. Introduction to Ray Tracing as a Rendering Technique
As a 3D rendering technique, ray tracing is an excellent tool for creating realistic and visually stunning graphics. Unlike other rendering techniques, ray tracing accurately models light transport, which means that it can provide more accurate results than other techniques. In my experience, ray tracing also gives artists more creative control over things like shadows, reflections, and refractions. In this blog, I'll explore the benefits and limitations of ray tracing, as well as the difference between ray tracing and light transport algorithms. As we move forward, we'll also look at the importance of ray tracing in modern movies and how it's being used to create faster and more efficient rendering techniques.

2. Understanding Path Tracing and Ray Tracing
Now that we've discussed the basics of ray tracing, it's important to understand the differences between ray tracing and path tracing. While both techniques involve tracing the trajectory of light to simulate realistic lighting and shadows, path tracing takes things a step further by tracing the paths of multiple light rays as they reflect and refract throughout a scene. This allows for more accurate simulations of complex lighting scenarios but comes with the drawback of being more computationally intensive than pure ray tracing. As a filmmaker and 3D renderer, I've found that understanding the nuances between these two techniques is crucial in creating realistic and visually striking scenes.
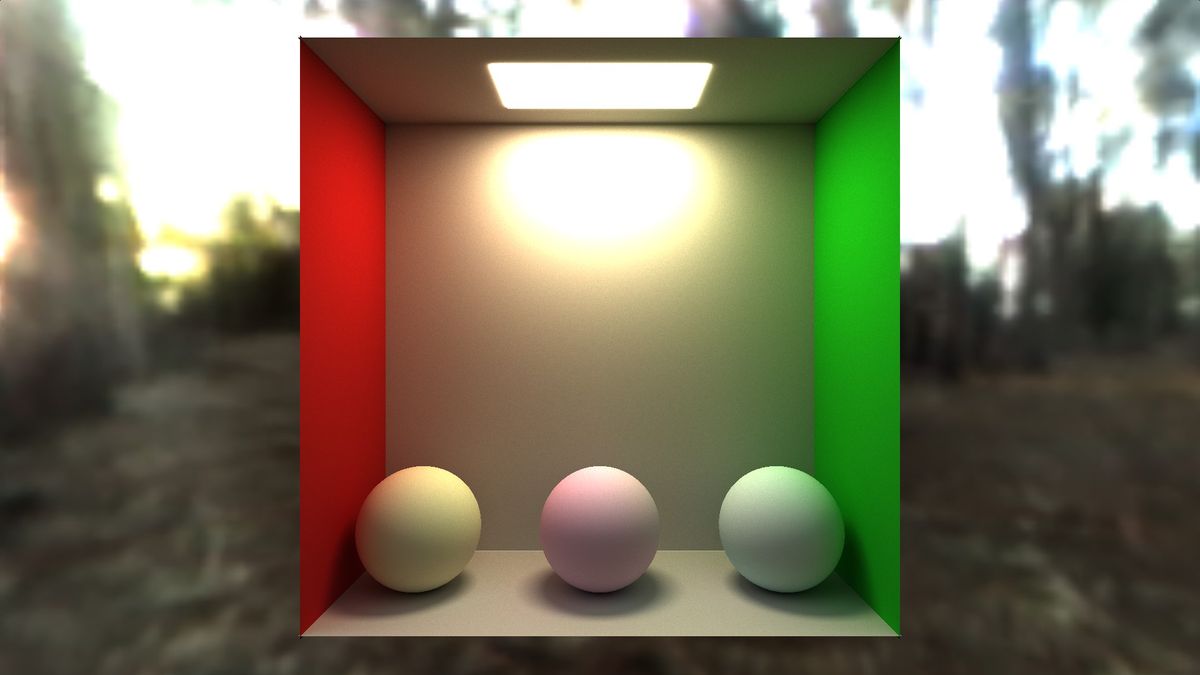
3. The Importance of Ray Tracing in Modern Movies
As I mentioned earlier, ray tracing has become a fundamental part of modern movie production. It's an efficient technique for generating or enhancing special effects with highly realistic reflections, refractions, and shadows. This makes it an extremely valuable tool for creating compelling, visually stunning scenes in film. The technology has come a long way in recent years and is now capable of providing high-quality renders and photorealism in the right situations. However, it's important to note that addressing noise artifacts is crucial when working with ray tracing, and various denoising techniques can be employed to overcome this issue. It's also worth mentioning that while ray tracing may be the superior choice for certain applications, it's not always the best option for every scene or object in a movie. Overall, the importance of ray tracing in modern movies cannot be overstated, and its contributions to the industry are undeniable.
4. Addressing Noise Artifacts in Ray Tracing
When it comes to ray tracing, one common issue is noise artifacts. These can appear when sampling light over a domain and can affect the overall quality of the finished image. There are ways to address this, however, including tracing a very large number of paths or using denoising techniques. Additionally, rendering noise can often be resolved over time as more path-tracing data is collected. While noise artifacts may be a concern, the benefits of ray tracing in terms of realism and the ability to simulate reflections, shadows, and refracted light make it a valuable tool in 3D rendering.
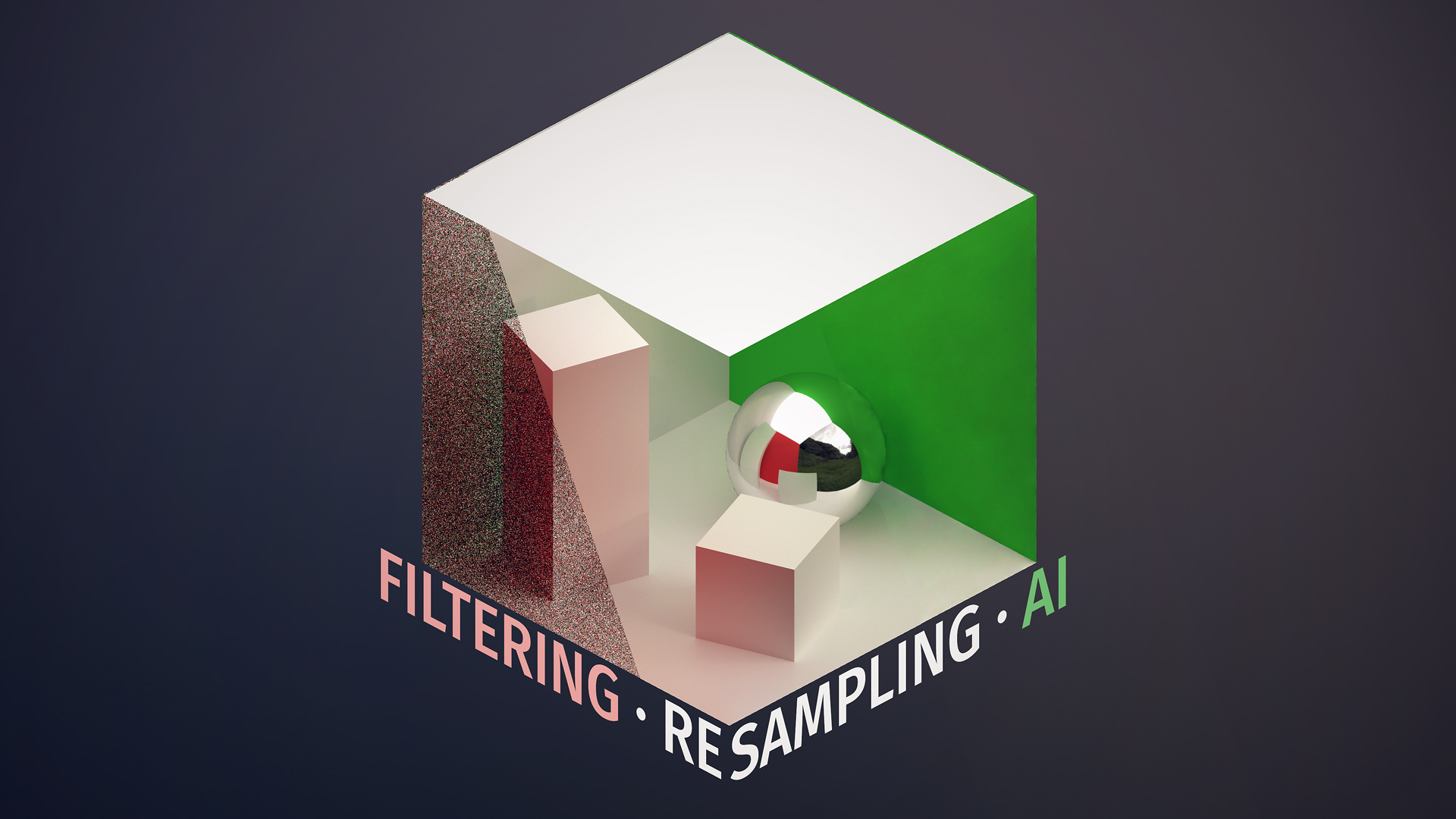
5. Denoising Techniques in Ray Tracing
As I mentioned in the previous section, image noise artifacts can be a critical issue in ray tracing. That's why denoising techniques are so important in this rendering technique. By removing undesired noise from ray-traced images, we can create high-quality images that are much more realistic. There are several denoising techniques available, including rendering the same frame over and over again, using Monte Carlo ray tracing, or implementing different shaders for various ray types. The overall goal is to create a satisfying approximation of a given scene by accumulating random samples, which are further processed to reduce image noise. Denoising is an essential and ongoing area of development in ray tracing because it helps address such issues and ultimately leads to generating more photo-realistic images at interactive rates.
6. Difference Between Ray Tracing and Light Transport Algorithms
As we have discussed earlier, Ray Tracing is a rendering technique that simulates the behavior of light in a scene by following a ray of light through it. On the other hand, Light Transport Algorithms use a different approach as they simulate the motion of photons in a scene. Both techniques have their own merits and demerits. Ray Tracing algorithms create realistic images with shadows and reflections that are visually accurate, while Light Transport Algorithms measure the light distribution in a scene and simulate real-world light behavior.
One of the most significant differences between the two techniques is in the way they handle indirect lighting. Ray tracing uses the path of the direct rays of light, which means they can miss the indirect lighting coming from bounced or reflected light. In contrast, Light Transport algorithms are intended to handle indirect lighting better, making them more accurate in simulated lighting.
In general, Light Transport algorithms are computationally more complex than Ray Tracing algorithms, making them more demanding in terms of processing power. However, modern advancements in computer hardware and software have allowed both techniques to achieve excellent results. Understanding the difference between these two rendering techniques is crucial for a 3D artist, game developer, or CG animator. By choosing the right technique or using a combination of both, the artist can make a realistic and visually appealing 3D render.

7. Realism and Benefits of Ray Tracing in 3D Rendering
As I've mentioned throughout this blog, ray tracing is a rendering technique that simulates the physical behavior of light, resulting in more realistic and accurate images. This technology has become increasingly important in modern movies, where CGI is used to create incredible special effects. The benefits of ray tracing extend beyond just the film industry, however. The technique allows shadows, reflections, and refractions to be precisely rendered, which adds a level of realism to 3D scenes that simply cannot be matched by other rendering algorithms. Additionally, ray tracing can be faster than other techniques, especially when motion blur is involved. However, it's important to note that there are limitations and drawbacks to consider when using ray tracing, such as noise artifacts and longer rendering times. Despite these potential issues, I believe that the realism and benefits of ray tracing make it a valuable tool in the world of 3D rendering.
8. Features of Ray Tracing: Shadows, Reflections, and Refractions
As we've discussed in previous sections, ray tracing is a technique for rendering images with an exceptional level of realism. One of the primary factors that contribute to this is the incredible accuracy with which it can simulate phenomena like shadows, reflections, and refractions. Shadows cast by objects in a scene are commonplace, but with ray tracing, they can be accurate to a level that was previously impossible. Similarly, reflections and refractions can be simulated with incredible attention to detail, making scenes look far more lifelike than with other rendering methods. These features are the hallmark of high-quality, photorealistic graphics, and with ray tracing, we're able to achieve them with ease. Whether used in film, video games, or architectural visualization, these features give us a window into the world we're creating that we couldn't get through any other means.
9. Ray Tracing for Faster Rendering with Motion Blur
When it comes to producing high-quality 3D renders, speed is always a concern. That's where motion blur and ray tracing come in. By tracing the path of every individual light ray in a scene, ray tracing can accurately simulate the way light behaves in the real world. This allows it to produce incredibly realistic shadows, reflections, and refractions. But ray tracing can also be used to speed up motion blur rendering. By only calculating the paths of rays that are moving, rather than every single ray in a scene, ray tracing can produce motion blur that’s just as accurate as traditional methods but is much faster. It’s just one of the many benefits that make ray tracing such a valuable technique in modern 3D rendering.
10. Limitations and Drawbacks of Ray Tracing Techniques
While ray tracing is an impressive rendering technique for creating realistic shadows, reflections, and refractions, it also has its limitations and drawbacks. One such drawback is the issue of noise artifacts in the rendered image, which can be caused by the algorithm's sampling method. This can be addressed using techniques such as denoising, which helps to eliminate noise in the final image. Additionally, ray tracing is computationally intensive and can be time-consuming, making it less suitable for real-time applications. However, advancements in technology have allowed for the use of ray tracing in gaming and other interactive applications. Overall, while ray tracing has its limitations and drawbacks, its benefits in achieving photorealistic and high-quality 3D rendering make it a valuable technique for many applications.