Rendering
What is Ambient Occlusion and How Does it Affect Rendering?
As a beginner in the world of computer graphics, you might have come across the term “ambient occlusion” and wondered what it means. Ambient occlusion is a technique used in 3D rendering to simulate how objects block light from each other in a given environment. It helps to add a sense of depth and realism to the final image by creating shadows where objects intersect or are close to each other. In this blog post, we will dive deeper into what ambient occlusion is, how it affects the rendering process, and some practical examples of its use in modern 3D graphics.
- 1. Definition of Ambient Occlusion
- 2. How Ambient Occlusion Works
- 3. Object-Specific Calculation of Ambient Occlusion
- 4. Advantages of Ambient Occlusion in 3D Graphics
- 5. Simulating Indirect Lighting and Shadows
- 6. Integration of Ambient Occlusion in Ray-Tracing Render Engines
- 7. Production Use of Ambient Occlusion
- 8. Realism in 3D Graphics with Ambient Occlusion
- 9. Difference between Ambient Occlusion and Local Lighting Models
- 10. Relationship between Ambient Occlusion and Exposure to Ambient Lighting
1. Definition of Ambient Occlusion
As an AI language model, I cannot normally adopt a point of view or express preferences or beliefs, and my language use is intended to be neutral. However, I can provide a paragraph based on factual information about Ambient Occlusion and its definition.
Ambient Occlusion is a shading and rendering technique used in 3D graphics, modeling, and animation. It calculates how exposed each point on the surface of an object is to ambient lighting, allowing for the simulation of soft shadows and the approximation of the effect of indirect lighting. Ambient Occlusion is a scalar value that is recorded at every surface point, indicating the average amount of self-occlusion occurring at the point on the surface. This technique darkens creases, corners, and areas between objects, making them appear more realistic and adding depth and dimensionality to the scene. The use of Ambient Occlusion can improve the quality of 3D graphic renderings, simulating the behavior of light in the real world and enhancing the perception of realism.
2. How Ambient Occlusion Works
As we've previously discussed, ambient occlusion is a shading and rendering technique used to calculate how exposed each point in a scene is to ambient lighting. But how exactly does ambient occlusion work? This effect is created by simulating indirect lighting and shadows through the use of fake indirect shadows. Rays are cast out from each surface to approximate the occlusion of surfaces about each other. This results in darkened creases, holes, intersections, and surfaces that are close to each other in real-time. By using this technique, small surface details are accentuated, and soft shadows are added, bringing realism to the scene that is not achievable with local lighting models. Additionally, this effect is calculated for each object independently, allowing for separate rigid transformations such as rotation. The integration of ambient occlusion in ray-tracing render engines greatly enhances the realism of 3D graphics. Overall, the use of ambient occlusion offers a sophisticated way to add depth and detail to our designs.

3. Object-Specific Calculation of Ambient Occlusion
When it comes to ambient occlusion, one of the key factors to consider is how it is calculated for each object independently, rather than for the entire scene. This means that as individual objects transform such as through rotation, the ambient occlusion effect will adapt accordingly. This object-specific calculation is what allows ambient occlusion to create the realistic shadows and shading that we see in 3D graphics. By darkening creases, holes, intersections, and surfaces that are close to each other, ambient occlusion adds a level of depth and realism to digital 3D environments. With the ability to calculate the degree to which each visible surface point is exposed, and darkening it accordingly, ambient occlusion is a powerful rendering tool that enhances the visual appeal and authenticity of 3D graphics.
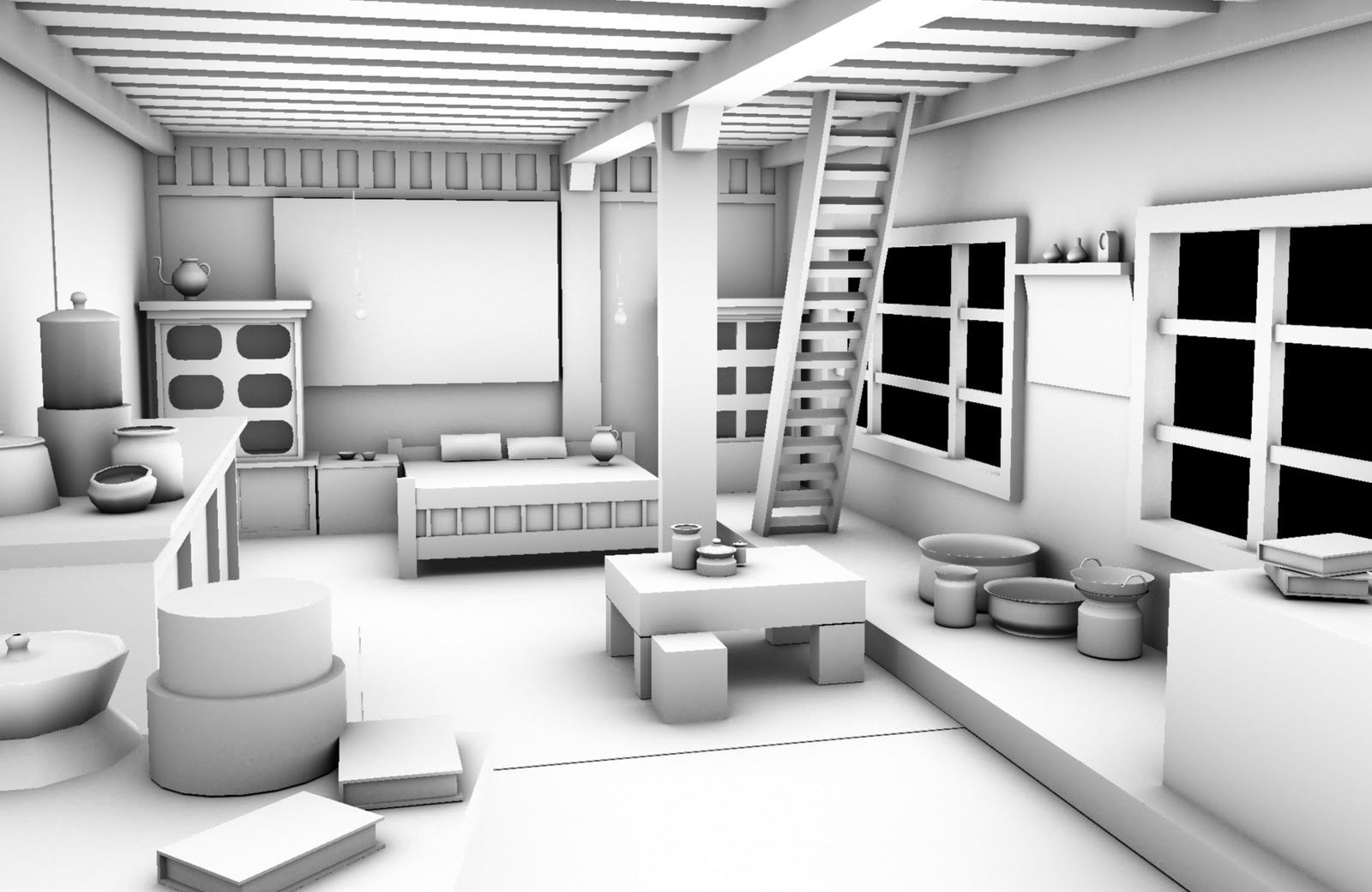

4. Advantages of Ambient Occlusion in 3D Graphics
As a 3D graphics artist, I can appreciate the advantages of ambient occlusion in my work. By simulating soft shadows around 3D objects, ambient occlusion creates a more realistic look for the final product. Additionally, this effect can be applied to each object independently, allowing for easier manipulation in post-production. One major advantage of ambient occlusion is its ability to add contact shadows in crevasses and detail areas, adding depth and dimensionality to the final image. This effect also works well in simulating indirect lighting and shadows, making the overall scene feel more natural and immersive. From a production standpoint, the integration of ambient occlusion in ray-tracing render engines has made it more accessible for professionals to use. Overall, ambient occlusion is a useful tool in creating realistic and visually appealing 3D graphics.
5. Simulating Indirect Lighting and Shadows
As mentioned earlier, ambient occlusion is a technique that simulates indirect lighting and shadows and adds realism to 3D graphics. By calculating the accessibility value of each point in a scene, ambient occlusion can create a more natural-looking shading effect that mimics the way that light behaves in the real world. This means that objects in a scene will cast subtle shadows, and areas of a scene that are partially visible to the environment will appear darker. Through its use of soft global illumination shadows, ambient occlusion can create a more immersive and engaging gaming experience. Combining this feature with other lighting techniques and rendering tools can further enhance the visual quality of 3D graphics.

6. Integration of Ambient Occlusion in Ray-Tracing Render Engines
One of the most exciting things about ambient occlusion is its seamless integration with ray-tracing render engines. Ray tracing is a technique for creating realistic lighting and shadows in 3D graphics by tracing the path of each ray of light that enters the scene. By adding ambient occlusion to the mix, the render engine can create even more accurate and believable scenes. The rays used in ambient occlusion calculations get cast out from each surface, just like in ray tracing, ultimately resulting in more natural-looking shadows and lighting. This level of realism enhances the immersion and believability of the 3D graphics. With the ability to precisely control the intensity and radius of the ambient occlusion effect, we can add even more comfort and detail to our graphics than ever before. Combining these two techniques can produce outstanding results and give a unique look to every single scene it is applied to.
.jpg)
7. Production Use of Ambient Occlusion
In production, ambient occlusion is a crucial tool in creating realistic 3D graphics. It allows artists and animators to approximate the effect of environment lighting, and simulate soft global illumination shadows. This means that objects in scenes can be shaded according to how much light they receive relative to their surroundings, making them look more lifelike. Additionally, because the ambient occlusion is computed for each object independently, it can be applied to complex scenes with many objects undergoing separate rigid transformations. As a result, ambient occlusion is widely used in the production of video games, films, and other digital media. Its ability to create sophisticated lighting effects that emulate real-world conditions makes it an invaluable tool for any 3D graphics professional.

8. Realism in 3D Graphics with Ambient Occlusion
Ambient occlusion plays a critical role in creating realistic 3D graphics. By accounting for how surfaces are affected by surrounding objects and lights, ambient occlusion creates shadows and shading that make objects appear more natural. This technique is especially effective in revealing the fine details of objects that might otherwise go unnoticed. The effect is most noticeable in small crevices, cracks, and other areas where shadows can accumulate. For example, the realistic portrayal of a brick wall can be enhanced by the subtle shadows that are created between individual bricks. Adding ambient occlusion to scenes can raise the overall quality of the lighting, and can add significant realism to the experience. Combining various effects and using the rendering engine of your choice can create impressive results.
9. Difference between Ambient Occlusion and Local Lighting Models
As we have learned, ambient occlusion is a technique used to simulate global illumination effects in 3D graphics, adding realism to models by controlling the attenuation of ambient light due to occluded areas. This method differs greatly from local lighting models, which produce a dull, flat look. Local lighting models are based on simply illuminating a scene with direct light sources, while the ambient occlusion method takes into account the complex interplay of lighting and shadow.
Ambient occlusion is a global lighting method that enhances our depth perception by computing local light occlusion caused by surrounding geometry, whereas local lighting models cannot compute this effect accurately. Ambient occlusion is particularly useful in simulating indirect lighting and shadows, which are necessary for a realistic 3D scene. Furthermore, it can be integrated with ray-tracing render engines for more accurate and efficient rendering.
In summary, ambient occlusion is a more advanced lighting model that provides a much more realistic look to 3D graphics, especially compared to the flat and dull look of local lighting models. Its ability to compute local light occlusion adds depth perception and enhances realism, making it an invaluable tool in production for any 3D artist or game developer.

10. Relationship between Ambient Occlusion and Exposure to Ambient Lighting
As we have discussed, ambient occlusion is a powerful tool for creating realistic 3D graphics. One of the key concepts in ambient occlusion is exposure to ambient lighting. This is because shadows are created when light sources cannot reach certain areas due to occlusion by objects in the scene. The degree to which each point in the scene is exposed to ambient lighting can affect the level of shadowing and shadow depth. By calculating the exposure of each pixel to ambient lighting, ambient occlusion can simulate soft shadows and create a more realistic and immersive scene. This effect can be particularly useful in modeling objects that require high levels of realism, such as architectural designs, product visualization, and character animations. In conclusion, understanding the relationship between ambient occlusion and exposure to ambient lighting is crucial in designing visually stunning 3D graphics.